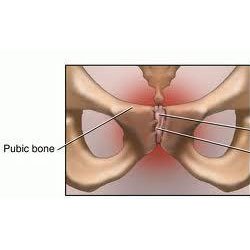
Osteitis pubis is an overuse type of injury which is characterized by inflammation of the pelvis at the connecting site of two pubic bones i e.
Osetitis pubis tight pelvic floor.
It is also known as pubic symphysitis.
Osteitis pubis can be infectious or non infectious condition in the pubis that is very painful.
It can lead to pelvic soreness or pain that can get worse with physical.
To put it simply joint hypermobility syndrome can be an ignored cause of chronic pelvic pain.
Much has been said about the importance of these muscles in women especially after giving birth.
The pelvic floor is made up of a group of muscles that run from the pubic bone at the front and the coccyx tailbone at the back.
Osteitis pubis is a painful inflammation of the pubic symphysis and the ligaments attached to it.
On each side these muscles attach to the ischial tuberosities bones you can feel if you place your hand underneath your buttocks when sitting.
A healthy correctly aligned pubis symphysis hardly moves at all.
Osteitis pubis is a noninfectious inflammation of the pubis symphysis also known as the pubic symphysis symphysis pubis or symphysis pubica causing varying degrees of lower abdominal and pelvic pain.
This joint is close to the body s midline.
Osteitis pubis osteitis pubis is a very serious condition involving the pubic symphysis joint that needs immediate attention.
The pubic symphysis is a thin joint that joins the two halves of your pelvis.
In childbirth it mainly appears post partum caused by a degree of trauma during the birth.
The pubic symphysis is the cartilage where the left and right pubic bones meet and is responsible for absorbing force between the two.
The pelvic bones form a ring with the pubic symphysis at the front and sacro iliac joints at the back.
Women with pop usually have pelvic floor muscle weakness which can be alleviated with physical therapy to the pelvic floor.
Osteitis pubis is a non infectious inflammation of the pubic symphysis resulting to lower abdominal and groin pain.
In postpartum women osteitis pubis is triggered by the instability of the pelvic bones which is exacerbated during pregnancy when the joints become lax due to the hormone relaxin.